Die Software hat den Embeddedbereich fest im Griff: diverse Aktualisierungen versuchen, das Leben des Systementwicklers zu erleichtern. Eine CVE gegen eine Race Condition in einem in Rust gehaltenen Kernelteil zeigt, was der Linuxwelt blüht. Was es sonst Neues gibt, vermelden wir – wie immer – in unserem News-Roundup-
MicroPython v1.27 unterstützt STM32U5, ESP32-C5 und ESP32-P4
Im Hause MicroPython steht eine – von der Versionsnummer her minimale – Aktualisierung an, die der p.t. Nutzerschaft sowohl neue Features als auch drei neue Zielplattformen eröffnet:
1 |
This release of MicroPython adds support for ESP32-C5 and ESP32-P4 microcontrollers. The ESP32-P4 can work either standalone as a general purpose processor, or with an external wireless co-processor, currently either an ESP32-C5 or ESP32-C6. Board profiles are provided for all three of these configurations, as well as for the new ESP32-C5. |
2 |
Support for the low-power and high performing STM32U5xx series is also added in this release, supporting USB, ADC, DAC, UART, I2C, SPI and RTC, with a board profile for the NUCLEO-U5A5ZJ-Q. |
Neuerung Nummero zwei betrifft die Einführung von vier Support Tiers, die sich wie in der Abbildung gezeigt präsentieren. Sinn davon ist die einfachere Ermittlung, “wie gut” MicroPython auf einer bestimmten Zielhardware funktioniert.
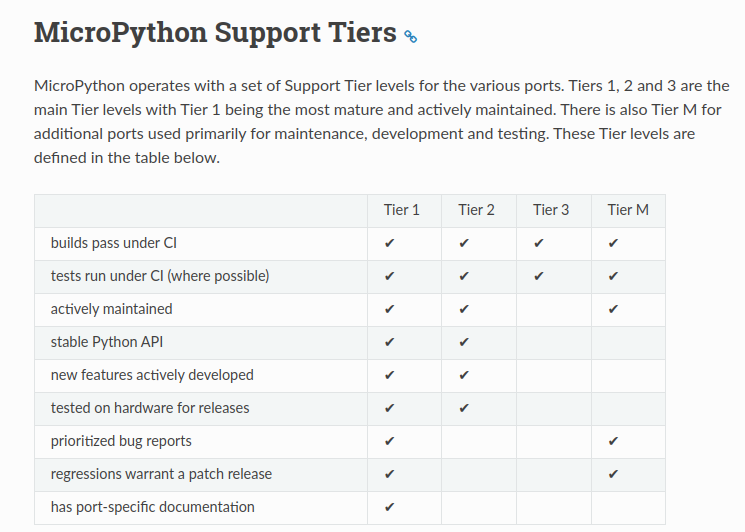
Bildquelle: https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/develop/support_tiers.html
Über die Anpassungen der Codegrößen vermeldet man dann das in der Abbildung gezeigte.
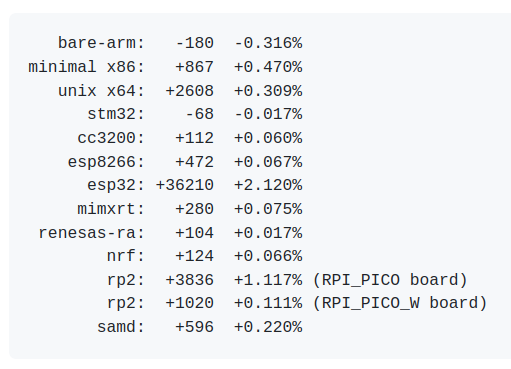
Bildquelle: https://github.com/micropython/micropython/releases/tag/v1.27.0
Weitere Informationen zu den diversen Detailverbesserungen finden sich in den als Bildquelle genannten URLs.
Erste CVE gegen Rust – “* CVE-2025-68260: rust_binder: fix race condition on death_list”
Proponenten der einst von Mozilla entwickelten, besonders inklusiven Programmiersprache predigen stets von den Sicherheitsvorteilen, die mit der Nutzung von Rust einhergehen. Nun gibt es – ausgerechnet in einem Unsafe-Block – die erste Race Condition:
1 |
… we just assigned our first CVE for some Rust code in the kernel: https://lore.kernel.org/all/2025121614-CVE-2025-68260-558d@gregkh/ where the offending issue just causes a crash, not the ability to take advantage of the memory corruption, a much better thing overall. |
2 |
--- via https://social.kernel.org/notice/B1JLrtkxEBazCPQHDM |
Die “Demokratisierung” der Wartung von Kernel-Infrastruktur ist offensichtlich ein zweischneidiges Schwert: desto niedriger die Einstiegsschwelle, desto höher das Risiko, sobald sich ein unsafe-Block öffnet…
Qt für Mikrocontroller – Version 2.12 verfügbar, bringt Maps-Implementierung mit Infineon
Im Hause Qt gibt es ebenfalls Neuerungen: Version 2.12, die letzte Version vor dem Umstieg auf 3.0, ist ab sofort verfügbar. Neben verschiedenen Aktualisierungen im Bereich Zephyr sticht folgende Ankündigung hervor:
1 |
we have developed a reference solution 'Navia' in collaboration with Infineon which provides state-of-the art native map and navigation experience on microcontrollers. This reference solution is not part of the official 2.12 release but built on top of our core product. It consists of multiple map provider integration like Mapbox, Google and OSM maps. |
2 |
--- via https://www.qt.io/blog/qt-for-mcus-2.12-lts-released |
Zu den in Version 3.0 zu erwartenden Änderungen vermeldet man folgendes:
1 |
No major QML API deprecation/overhaul is expected, so a transition path from 2.x applications will be smoother. A comprehensive guide will be provided. |
2 |
A major version upgrade to the C++17 standard is planned, to leverage some of the advanced security features for CRA compliance. |
3 |
For digital products built on resource-constraint hardware, connectivity is a key aspect and we are working on a solution to streamline the data flow between HMI and a companion app over a BLE connection. |
4 |
Qt for MCUs 3.0 will be a fully CRA-compliant release available in mid-2026. Until then a comprehensive list of changes in version 2.12 can be found in the changelog. |
SemTech: Unified Software Platform (USP) für LoRA in Version 1.0 verfügbar
Im Hause SemTech gibt es ein (kleines) Softwareupdate – die als Abstraktionsschicht dienende Unified Software Platform steht unter https://github.com/Lora-net/USP?u ab Sofort als Version 1.0 zur Verfügung.
Wireless-Tag WTDKP4C5-S1 – kompakteres ESP32-P4-Modul mit Funkfunktion
Espressif’s Hochleistungs-Mikrocontroller kommt – bekannterweise – ohne Funkmodul zum Entwickler: ein Problem, dem durch verschiedene Cx-ESP32-Versionen Abhilfe geschaffen werden kann.
Espressif’s mit Sicherheit aktivster Distributor Wireless-Tag bietet nun ein Modul an, in dem ESP32-P4 und ESP32-C5 sowie ausreichend Arbeitsspeicher kombiniert sind. Ziel ist die Vereinfachung der Integration der (von ESP-IDF excellent unterstützten) Kombination in Applikationsschaltungen.
Bildquelle: http://en.wireless-tag.com/product-item-73.html
Maxell: neue, säurefreie Knopfzellenbatterie
Maxell arbeitet seit 2019 an Feststoffbatterien im Knopfzellenformat. Mit der PSB2032 steht nun eine neue Variante ante Portas (Samples ab Dezember), die eine höhere Kapazität bietet.

Über die sonstigen Spezifikationen vermeldet man folgendes:
1 |
To meet these market needs, Maxell has newly developed the “PSB2032”, a coin type all-solid- |
2 |
state battery designed to be suitable as the main power source for IoT devices. The battery |
3 |
features 20 mm in diameter and 3.2 mm in height. |
4 |
Since developing coin type all-solid-state battery in 2019, Maxell has been advancing research |
5 |
and development of all-solid-state batteries of various types, including ceramic package type, |
6 |
bipolar type, and cylindrical type. The newly developed “PSB2032” delivers a capacity of 35 |
7 |
mAh - approximately four times that of the ceramic- packaged “PSB401010H” currently in |
8 |
mass production, making it suitable for use as the main power source for IoT devices. |
DHRUV64 – erster indischer 1GHz-Zweikernprozessor
In Indien nutzt man die RISC/V-ISA zur Realisierung von hauseigenen Prozessoren. Nun steht ein Zweikernchip ante Portas, der komplett in Indien entwickelt und gefertigt wurde.

Bildquelle: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?id=156505&NoteId=156505&ModuleId=3®=6&lang=1
Ziel dürfte hier weniger die kommerzielle Nutzung sein. In der Ankündigung finden sich vor Allem Verweise darauf, dass der Chip erstens strategische Bedeutung hat und zweitens bei der Entwicklung von noch leistungsfähigeren Prozessoren als Sprungbrett dienen soll:
1 |
Strategic Significance of DHRUV64 for India |
2 |
DHRUV64 marks a major milestone in India’s efforts to build a secure and self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem. It strengthens the nation’s indigenous capability in advanced processor development. It supports the critical digital infrastructure and hence, reduces the long-term dependence on imported microprocessors. |
3 |
India consumes around 20% of all the microprocessors manufactured globally. The development of DHRUV64 provides India’s large talent base with a fully modern processor platform for advancement of semiconductor ecosystem in India. |
4 |
Before DHRUV64, India had already begun expanding its indigenous microprocessor development ecosystem in recent years. Key examples include: |
5 |
• SHAKTI (2018, IIT Madras): Designed for strategic, space, and defence applications; |
6 |
• AJIT (2018, IIT Bombay): A microprocessor for industrial and robotics applications; |
7 |
• VIKRAM (2025, ISRO–SCL): A processor developed for space applications such as navigation, guidance, and mission operations; engineered to withstand extreme space conditions; |
8 |
• THEJAS64 (2025, C-DAC): Designed for industrial automation. |
9 |
Developing indigenous processors such as the SHAKTI, AJIT, VIKRAM, THEJAS, and now the DHRUV64 is strategically significant. These processors drive the creation of an Indian processor ecosystem. |
10 |
DHRUV64’s Impact on India’s R&D and Innovation |
11 |
• DHRUV64 provides a homegrown microprocessor technology designed for startups, academia, and industry to build, test, and scale indigenous computing products without relying on foreign processors. |
12 |
• DHRUV64 supports prototype development for new system architectures at lower cost. |
13 |
• India already has 20% of the world’s chip design engineers. DHRUV64 further helps in building a strong pipeline of skilled semiconductor chip professionals. |
14 |
• The success of DHRUV64 accelerates the roadmap for Dhanush and Dhanush+ processors. They are now under development phase. |
Rohde und Schwarz – RF-Leistungssensor mit 170GHz Grenzbandbreite
Mit dem NRP150T schickt Rohde und Schwarz einen neuen thermischen Leistungssensor ins Rennen, der alle automotiven Radarbänder abdecken kann. Weitere Informationen finden sich unter der als Bildquelle angegebenen URL.

Interessant ist außerdem, dass dieser Sensor nicht nur im Zusammenspiel mit Messtechnik verwendbar ist. MWJ berichtet unter https://www.microwavejournal.com/articles/45130-rohde-and-schwarz-presents-r-and-s-nrp150t-thermal-power-sensor von der Verfügbarkeit einer Android-Applikation:
1 |
It is easy to use thanks to USB connectivity, compatible with standard PCs and Android mobile devices using a free remote control app, or through the R&S NRX base unit from Rohde & Schwarz. |
Target 3001 – im Zeichen der künstlichen Intelligenz
Im Rahmen der alljährlichen Weihnachts-Email informiert IBF seine Kunden nach folgendem Schema darüber, dass die nächste Version des Produkts mehr AI-Funktionen mitbringen wird:
1 |
Das kommende Jahr 2026 wird neben vielen neuen Features auch das Jahr der KI in TARGET werden. Spannende und bis vor kurzem undenkbare Ideen und Konzepte werden in TARGET einfließen und Ihnen die tägliche Arbeit erleichtern. Darauf freuen wir uns! |
NXP – fortan ohne 5G-Leistungsverstärker
Marktbreite belebt das Geschäft – in Sachen 5G-Leistungsverstärker gab es schon bisher nur vergleichsweise wenige Marktteilnehmer. LightReading berichtet unter https://www.lightreading.com/semiconductors/nxp-to-exit-5g-with-closure-of-radio-power-fab-in-arizona?ut nun darüber, dass sich NXP aus diesem Marktsegment zurückzieht:
1 |
"5G rollout declined in recent years due to a lack of return on investment for mobile operators and global 5G basestation deployments have been well below original estimates," said the company in an email sent to Light Reading. "Given the market realities with no outlook for recovery, the RP business no longer fits into the company's long-term strategic direction. Therefore, NXP has made the decision to ramp down its Radio Power product line." |
Lesestoff: USB 2.0 im Zeitalter von USB-C
USB 2.0 ist auch heute noch von Relevanz. Same Sky – einst als CUI bekannt – bietet unter https://www.sameskydevices.com/blog/usb-2-0-is-not-dead nun einen Artikel an, der auf die Coexistenz zwischen USB 2.0 und USB-C-Steckern eingeht.
Lesestoff, zur Zweiten – Call for Papers für European Microwave Week
Wer sich für Amateurfunk und HF-Technologie als Ganzes interessiert, dürfte die European Microwave Week als interessant empfinden. Nun startet der Call for Papers, der – wie in der Abbildung gezeigt – nach Papers und Vorträgen zur Thematik sucht.

Bildquelle: https://www.eumw.eu/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/4997_eumw2026_call_for_papers-06.pdf
Lesestoff, zur Dritten – zur Besteuerung von ständigen Niederlassungen
Unter https://wtsklient.hu/en/2025/12/12/pe-study-of-wts-global-released/ findet sich eine durchaus lesenswerte Zusammenstellung, die die rechtliche Situation in rund 70 Jurisdikationen zusammenfasst. Eine ständige Niederlassung kann in manchen Fällen Administrationsaufwand einsparen, weshalb sich ein Blick lohnt…
Zuerst erschienen bei Mikrocontroller.net News
Quelle: Weiterlesen
